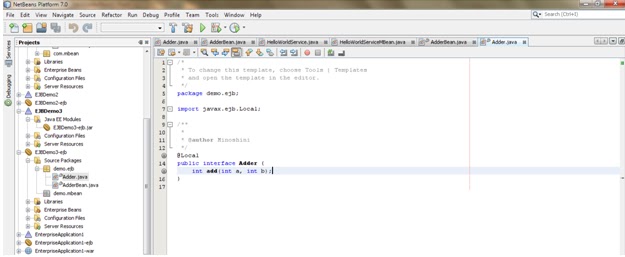
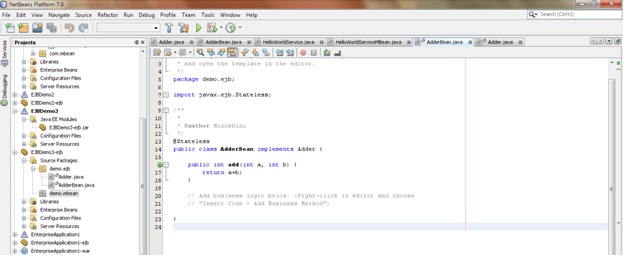
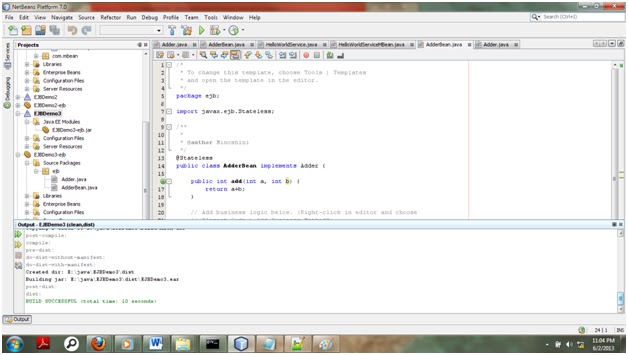
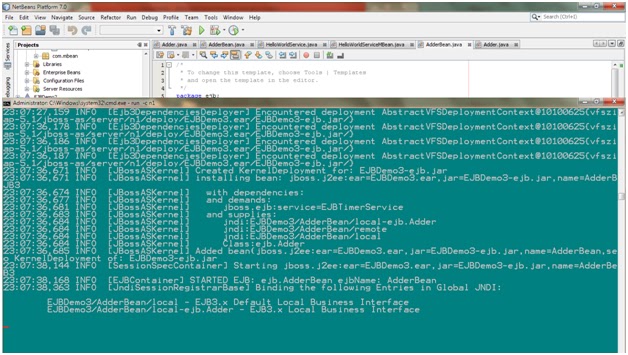
I will demonstrate this with a simple HelloWorld java program.
1. 1. First write HelloWorld program in java.
/*
* To
change this template, choose Tools | Templates
*
and open the template in the editor.
*/
/**
*
*
@author MiFoLK
*/
public class HelloWorld {
public static String hello(){
return "hello world !!";
}
}
2.
Then we have to load the java class in Oracle
database using loadjava tool. So we have to copy the HelloWorld.java to the bin
folder of the oracle. We have to give username and password.
Eg:
loadjava
-u user_name/password -v -resolve HelloWorld.java
 |
| Figure 1 |
Further
we can verify the compilation and load with a simple query against user
objects. If it is done correctly the status is showing as valid.
 |
| Figure 2 |
3. Publish the java class in Oracle database.
Now I have used P/L Sql Develper to write
the function where the java class is called.
Basically it is done in this way.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION
hello_func(varchar2 pubkey)
-- Declare a data base function called
hello_func which takes a varchar2 param and returns ---------varchar 2
RETURN varchar2
-- This function should be declared
according java function
AS LANGUAGE JAVA
NAME 'HelloWorld.hello(java.lang.String)
return String';
--Map the java function with database
function.
This is how I applied it into my simple
example.
 |
| Figure 3 |
3.1
Open a new SQL Window and type this Query.
3.2
Then execute the query.
3.3 Go to Objects window and refresh the functions
folder.
3.4 Then
HELLO_FUNC function will appear.
1. 4. Calling P/L SQL procedure.
4.1
Right click on HELLO_FUNC function and click
test.
4.2
Then you can see a test script.
 |
| Figure 4 |
4.3 Once you execute it you can see the result of
the program.
 |
| Figure 5 |
In this manner you can execute java programs via oracle p/l sql query. :)